After eight years spent studying a 1.8-million-year-old skull uncovered in the republic of Georgia, scientists have made a discovery that may rewrite the evolutionary history of our human genus Homo.
After eight years spent studying a 1.8-million-year-old skull uncovered in the republic of Georgia, scientists have made a discovery that may rewrite the evolutionary history of our human genus Homo.
It would be a simpler story with fewer ancestral species. Early, diverse fossils — those currently recognized as coming from distinct species like Homo habilis, Homo erectus and others — may actually represent variation among members of a single, evolving lineage.
In other words, just as people look different from one another today, so did early hominids look different from one another, and the dissimilarity of the bones they left behind may have fooled scientists into thinking they came from different species.
This was the conclusion reached by an international team of scientists led by David Lordkipanidze, a paleoanthropologist at the Georgian National Museum in Tbilisi, as reported Thursday in the journal Science.


 In the middle of the 7th century, a plague swept through the walled city of Jerash,...
In the middle of the 7th century, a plague swept through the walled city of Jerash,... A newly discovered species of large dinosaur lived in marshy areas, hunted for fish and had...
A newly discovered species of large dinosaur lived in marshy areas, hunted for fish and had...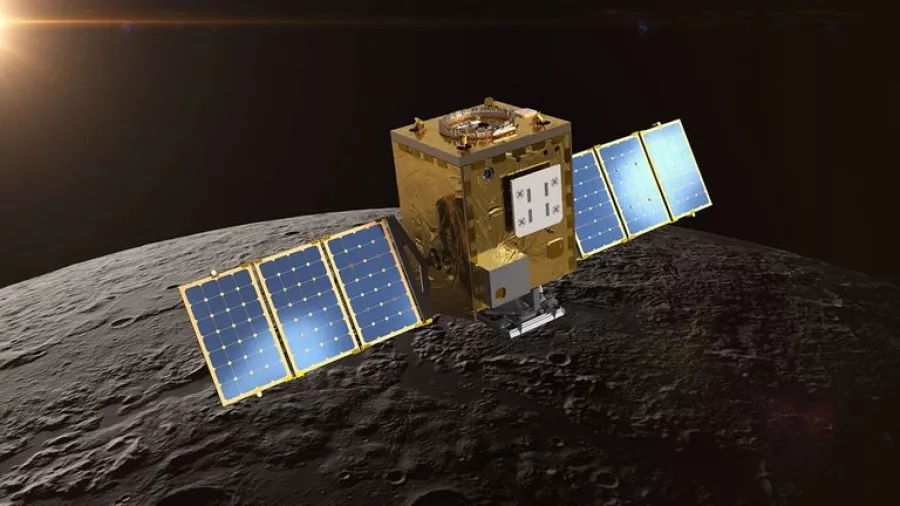 On February 26, 2025, a NASA probe called Lunar Trailblazer lifted off from Kennedy Space Center...
On February 26, 2025, a NASA probe called Lunar Trailblazer lifted off from Kennedy Space Center...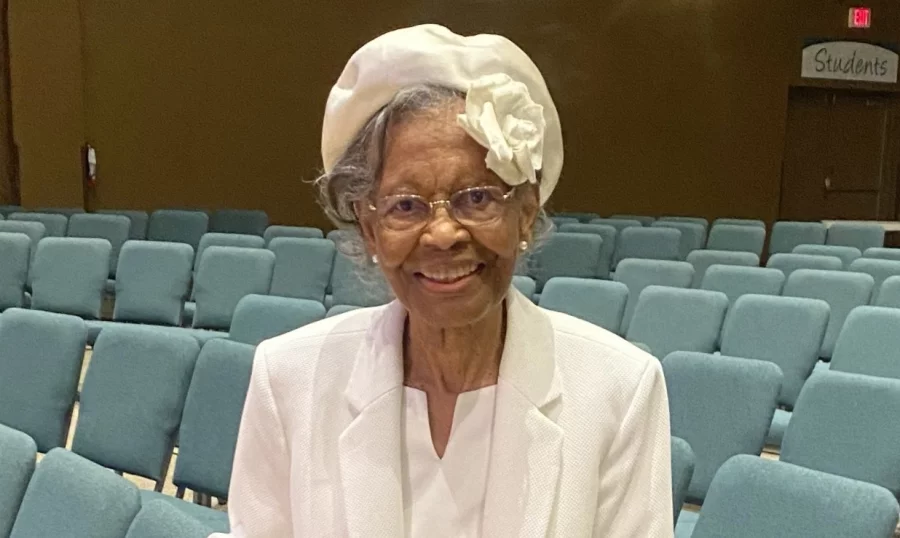 She navigated segregation to become an esteemed mathematician — and today, her work helps billions of...
She navigated segregation to become an esteemed mathematician — and today, her work helps billions of...